How does the Vegetation Index work?
How does the Vegetation Index work?
Growing plants absorb blue and red light and then reflect green light, which is why they appear green to the human eye. Plants also reflect near-infrared (NIR) light, but it’s invisible to the human eye. The higher the vegetation index of the plant, the more NIR is reflected. When a plant becomes stressed, its leaves reflect less NIR light. Wide Dynamic Range Vegetation Index, or WDRVI, measures the difference between red and near-infrared light bands reflecting off vegetation in the field to assess the amount of chlorophyll that is present and active in the plant at any given time up to three times more accurately than NDVI. This analysis is the basis of the Vegetation Index in Granular Insights.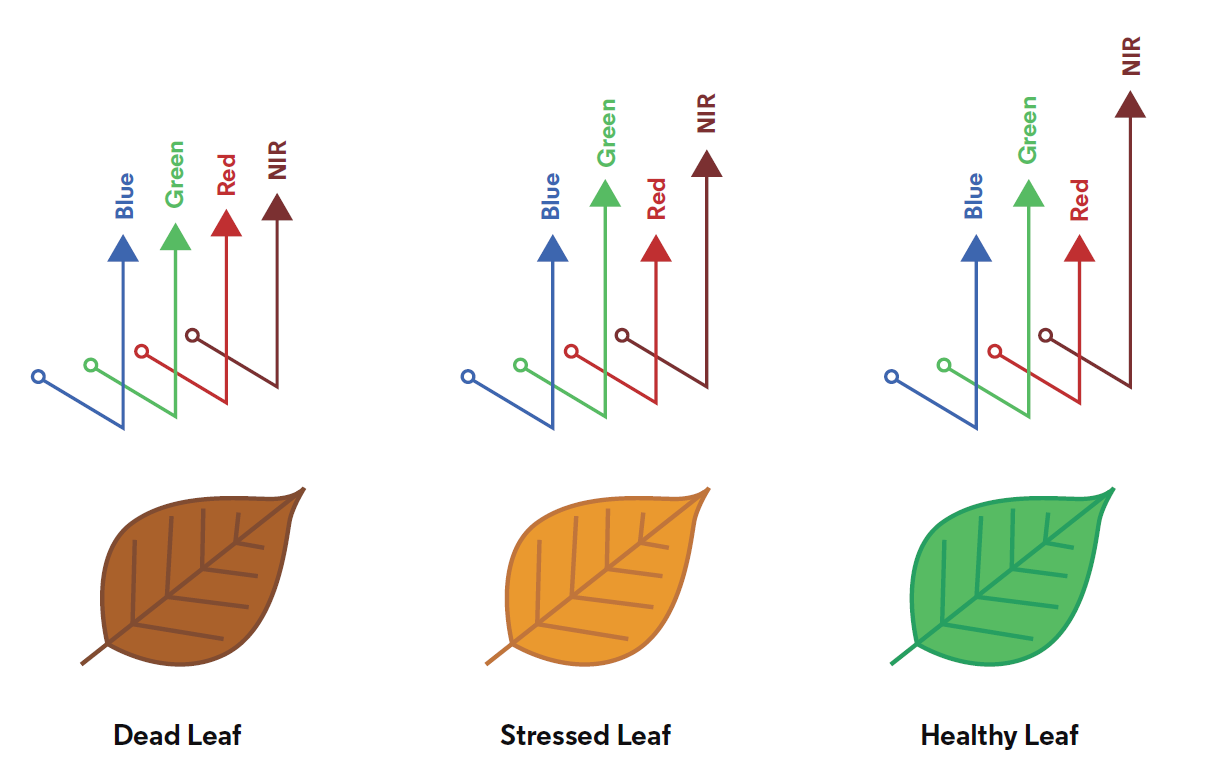
Was this article helpful?
0 out of 0 found this helpful